Learning is thought to be an
associative process between a stimulus and a response. The stimulus may be an action
involving any motive which compels an organism to show an action to a
particular stimulus known as a response. In classical conditioning, a stimulus
occurs first followed by a response. There are some terms mainly used in
classical conditioning such as neutral stimulus, unconditional response,
conditional stimulus, conditional response, stimulus extinction, stimulus generalization,
instantaneous recovery, and so on. All these terms are the processes that happen
in classical conditioning which are defined as given below.
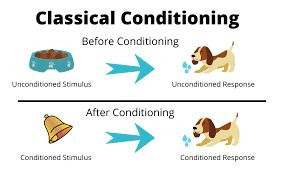
Neutral stimulus:
An action that
creates no response in an organism.
Unconditional stimulus:
An action that creates a response first time
in an organism in combination with another stimulus.
Unconditional response:
The action
or response is created in an organism first time as a result of an
associative stimulus.
Conditional stimulus:
An action
that creates a response in an organism without a combination with another
response.
Conditional response:
A response is created in an organism by a conditional stimulus without a combination
of another response.
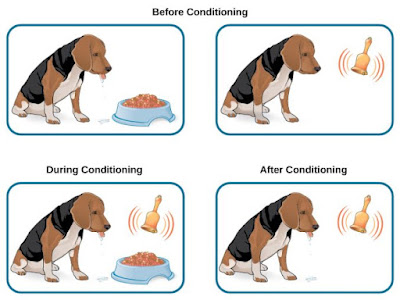
In classical conditioning, a
neutral stimulus in association with another stimulus creates a conditional
response. When a neutral stimulus is presented to an organism for the first time,
there will be no response created in an organism at all. When this stimulus is
paired with another stimulus that is familiar to the organism, it creates a
response the first time. When this exercise is carried out repeatedly three to four
times or even more, then there will be always a response which is called a conditional
response. Now, if the stimulus which was neutral initially but is now paired is
presented to the same organism without pairing with another stimulus, still
there will be a response shown by the organism. That is how the classical
conditioning process occurs in all organisms.
When classical conditioning is
created in an organism and the same practice is carried out with the organism
then there will be a time that organism gradually loses the conditioned
response and it will be finished. That process is called extinction. While sometimes,
it is possible that instead of an actual conditional stimulus, a similar stimulus
is presented to the organisms, still the organism shows a response. This process
is called stimulus generalization. When the same similar stimulus is presented, again and again, the organism feels the difference between the original
conditional stimulus and a similar presented stimulus and does not show a response,
such process is called stimulus discrimination. If ones, the conditional-response
is extinct, then it can be again created in the organism by presenting the
original conditional stimulus. This process is called the instantaneous recovery of
conditional response.
In schools, learning takes place
through classical conditioning. According to Aristotle who had the notion that
people remember or learn things when things are similar to each other or
things are in contrast to each other or learning takes place easily when two
things are contiguous with each other. Thus, the last statement which is about contiguity
is dominant even in today’s classrooms. On the basis of this contiguity, the classical
conditioning theory of learning has been constructed.
Understanding classical
conditioning for teachers is important as it can be helpful to plan their lessons
accordingly. The teachers can easily develop their intended behaviors among
the students in topics of their subject areas that are best suited for
classical conditioning.
Broadening Horizons


0 Comments
Post a Comment